| t >> |
|
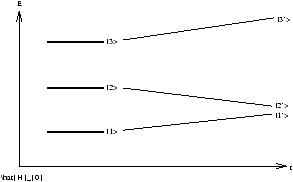
Figure 22.1 - Eigenstates and Energies Evolving Smoothly
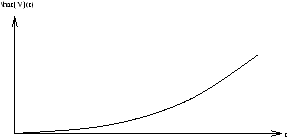
Figure 22.2 - V(t) Evolving Smoothly
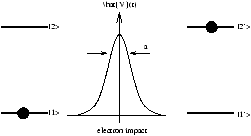
Figure 22.3 - A Fast Collison
| Y (0)+U1(r | )e |
|
® Y (t)=aU1(r,t)+bU2(r,t) |

|
Y (r,t)=HY (r,t) (23.1) |
| Yn(r,t)=un(r | )e |
|
(23.2) |
| <A | >= | ó õ |
|
Y*(r,t)AY (r,t)dV |
|
<A | >= | ó õ |
|
é ê ê ë |
Y*(r,t) |
|
AY (r,t)+ |
|
AY (r,t)+Y*(r,t)A |
|
ù ú ú û |
dV (23.3) |
|
=- | HY (r,t) |
|
= | ( | HY (r,t) | ) |
|
(23.4) |
| ó õ |
|
( | HY (r,t) | ) |
|
AY (r | ,t)dV= | ó õ |
|
Y*(r,t)HAY (r,t) |
|
= | ó õ |
|
Y*(r,t) |
|
Y (r,t)dV+ | ó õ |
|
Y*(r,t)[HA-AH]Y (r,t)dVº [H,A] |
|
= |
|
+ | <[H,A]> (23.5) |
|
=0 (23.6) |
| px=- |
|
|
= | <[H,px]> (23.7) |
| Þ |
|
= |
|
=- |
|
(23.8) |
| - |
|
= |
|
|
= | <[H,A]>=0 (23.9) |
|
=[H0+V(t)]Y (r,t) (23.10) |
| t >> |
|



| Y (0)+U1(r | )e |
|
® Y (t)=aU1(r,t)+bU2(r,t) |


