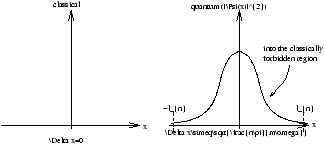
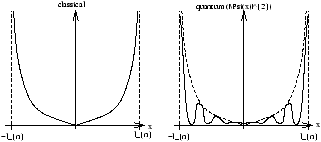
Figure 15.1 - For a Low n State

| Yn(b )µ (A | )nY0(b ) (16.1) |
| Yn(b )= |
æ ç ç è |
|
ö ÷ ÷ ø |
|
C0Hn(b )e |
|

|
æ ç ç è |
n+ |
|
ö ÷ ÷ ø |
w = |
|
mw2ln2 |
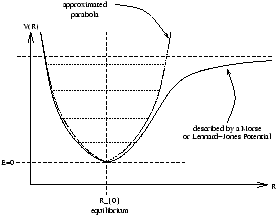
| V(R)= |
|
mw2(R-R0) (16.2) |
| V(x)= |
|
mw2x2 |
| E0= |
|
w |
| En= |
æ ç ç è |
n+ |
|
ö ÷ ÷ ø |
w |
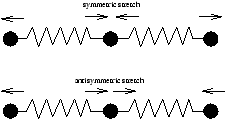
| Em= |
æ ç ç è |
m+ |
|
ö ÷ ÷ ø |
wq (16.3) |
| <E>q= |
|
(16.4) |
| Þ <E>q= |
|
+ |
|
wq (16.5) |
| En= |
æ ç ç è |
n+ |
|
ö ÷ ÷ ø |
w |


