
Chapter 8 Convention
-
Ivy
- inertial observer on playground
- Rosy
- rotating observer on roundabout
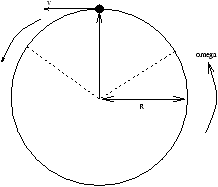
8.1 Radial Motion
Ball projected from the centre to rim ( v»w R )
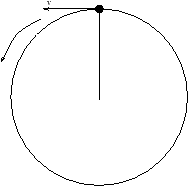
Ivy's Observation
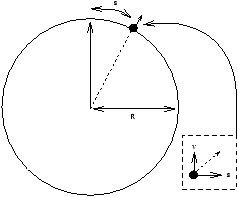
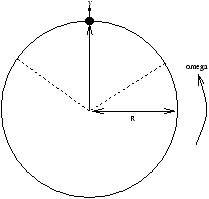
Rosy's Observation
Time to reach the rim t=R/v , the sideways deflection s=(w R)t=1/2at2 where a is the sideways acceleration. Substitute this for t
ie sideways force F=ma=2mw v which is known as the Cariolis Force. This is a fictitious force due to working in a non-inertial frame.
Recall for circular motion
v (speed)=w R
r (position)=Rcos (w t)i+Rsin (w t)j
| r=-w2r=-w2Rr= |
æ
ç
ç
è |
|
|
ö
÷
÷
ø |
r |
8.1.1 Ivy's Observation
8.1.2 Rosy's Observation
v=v'+w R
where:
-
-2v'w
- cariolis force
- -w2R
- centrifugal force
8.2 Tangential Motion
Project a ball round the circumference of the roundabout
v=v'+w R
from circular motion
acceleration = a' + cariolis + centrifugal
Acceleration measured by Rosy in her frame so
a'=a+2w v'+w2R
NB Cariolis and Centrifugal act radially outwards in this case
8.3 Rotating Frames in General
In time D t , R rotates an angle w D t . The change in the particles position r in Ivy's frame due to rotation of Rosy's frame
|D r1|=w rsin q .D t
Direction of D r1 is parallel to w× r
D r1=w× r D t
If the particle is moving in R and moves D r2 in time D t then the total displacemnt observed by Ivy is
D r=D r1+D r2=D R+2+(w× r)D t